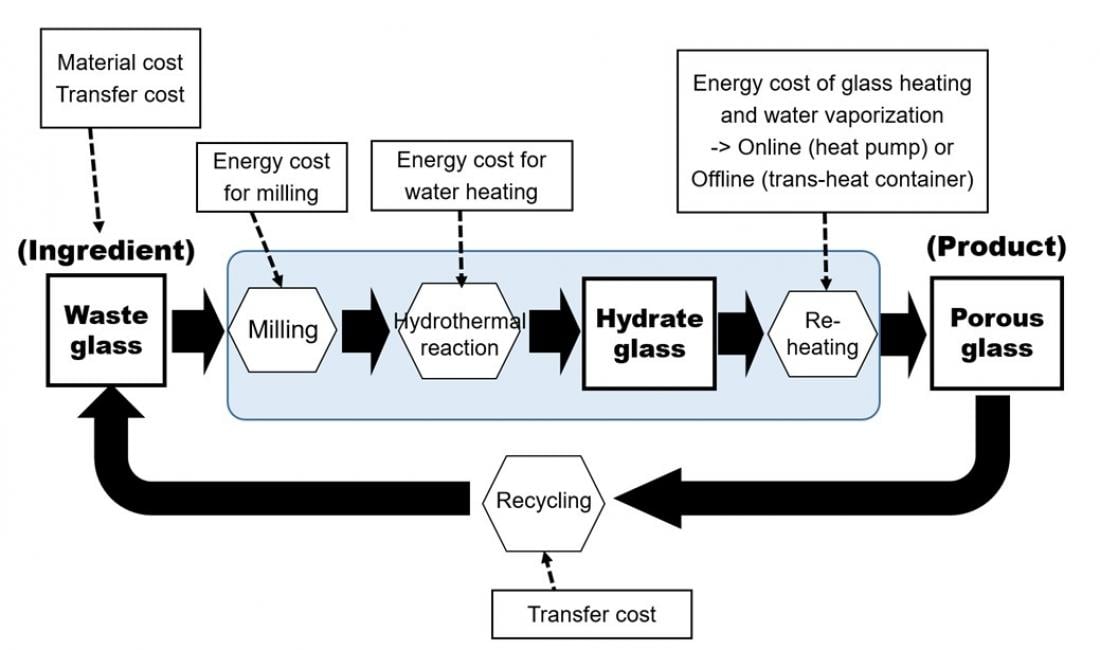
Processes of manufacturing using hydrothermal technology
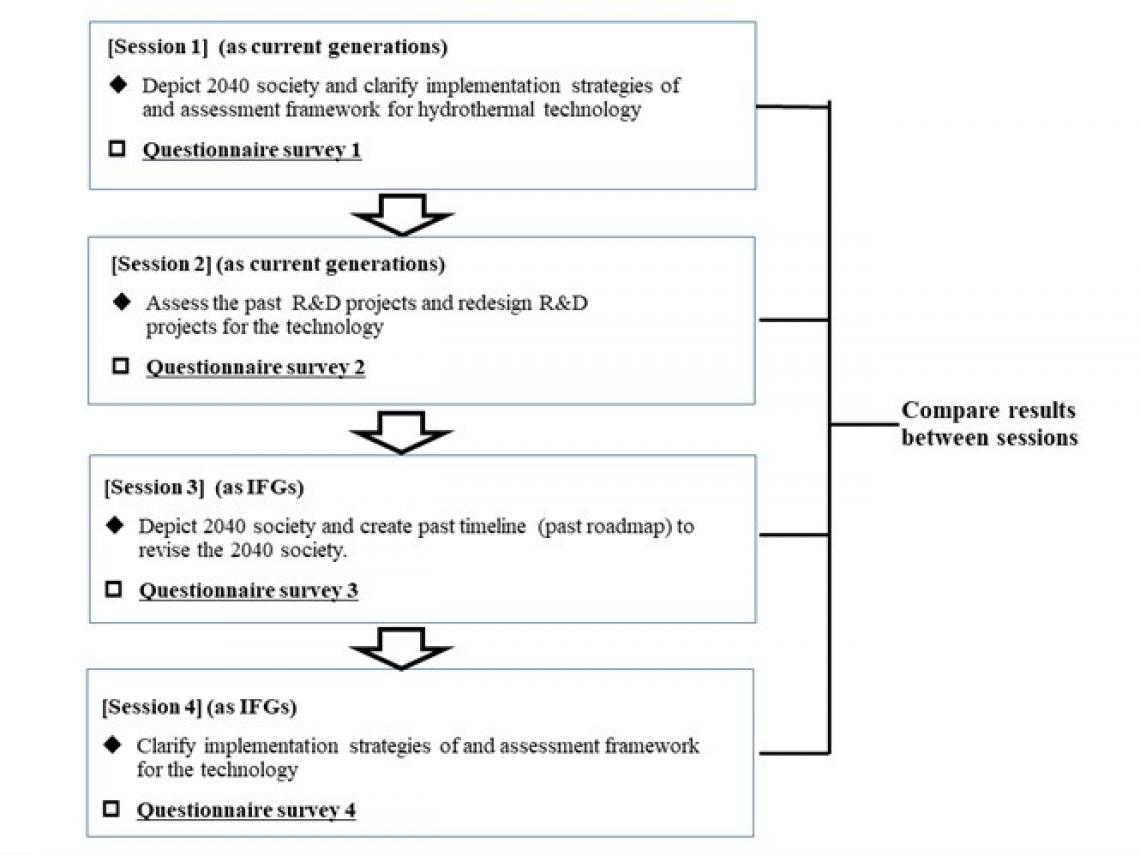
Flow of workshop (deliberation experiment)
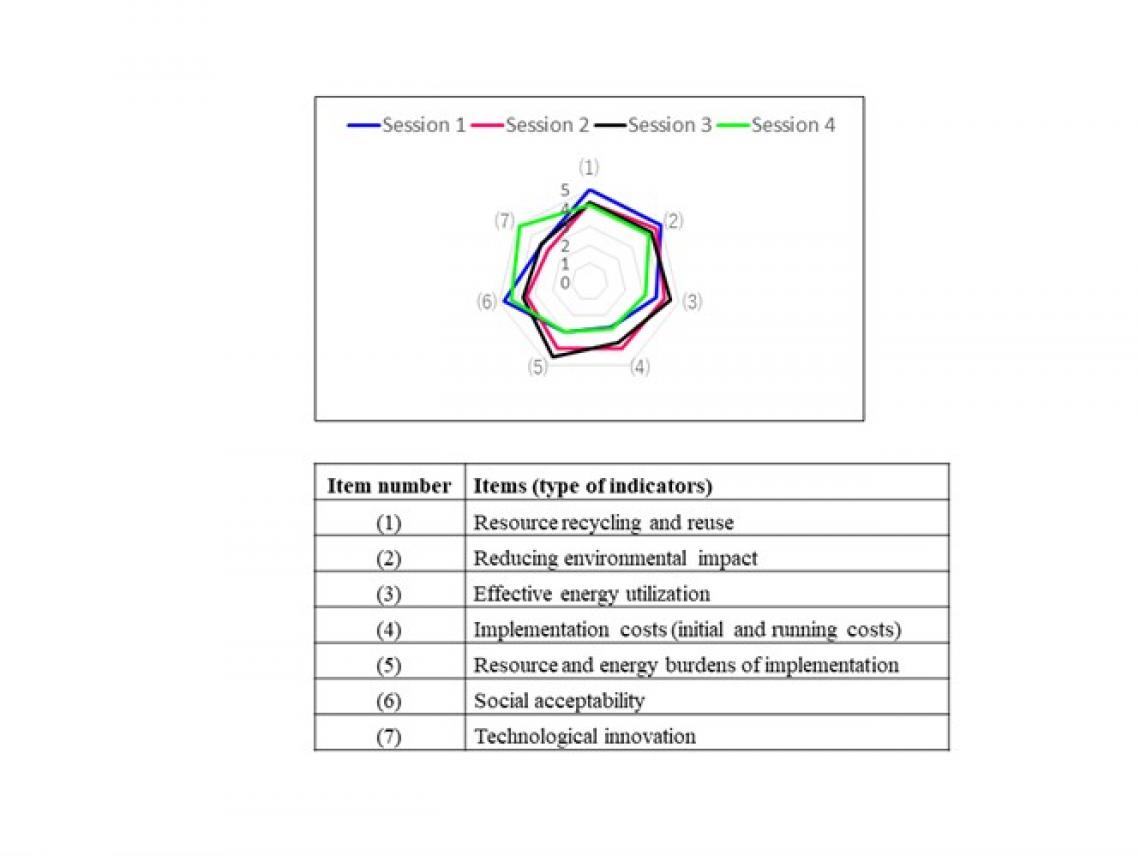
Results of technology assessment based on questionnaire survey (Group A)
(Change in mean scores for each item among sessions)
Researchers from Osaka University find that thinking about issues of sustainability from the perspective of “imaginary future generations” yields insights into technological innovation and societal trends
Osaka, Japan – The world approaches an environmental tipping point, and our decisions now regarding energy, resources, and the environment will have profound consequences for the future. Despite this, most sustainable thought tends to be limited to the viewpoint of current generations.
In a study published in Technological Forecasting and Social Change, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that adopting the perspective of “imaginary future generations” (IFGs) can yield fascinating insights into long-term social and technological trends.
The researchers organized a series of four workshops at Osaka University, with participants drawn from the faculty and student body of the Graduate School of Engineering. The workshops discussed the state of future society and manufacturing in general, and also looked at one technology in particular: hydrothermally produced porous glass. During the workshops, the participants were asked to think about this technology from the perspective of IFGs, to imagine how this technology might be adopted in the future and to assess its future potentiality.
“We chose hydrothermally produced porous glass for the case study because of the generational trade-offs involved,” says lead author of the study Keishiro Hara. “Porous glass is incredibly useful as either a filter for removing impurities or an insulator for buildings. Also, it can be recycled into new porous glass more or less indefinitely. The problem is that making it takes a lot of energy – both to pulverize waste glass and to heat water to very high temperatures. There’s a striking trade-off between costs now and gains in the future.”
In the workshops, the participants first looked at issues involving society and manufacturing from the perspective of the present and were then asked to imagine themselves in the shoes of their counterparts in 2040.
“The future the participants imagined was quite different from the future as seen from the perspective of the current generation,” explains Toshihiro Tanaka, senior author. “Most groups described a future in which sustainability has become a central concern for society. Meanwhile, advances in renewal energy mean that energy is abundant, as are resources, as frontiers such as the moon and deep ocean are opened to exploration. In this context, hydrothermally produced porous glass comes into its own as a sustainable way to recycle glass, and the energy needed to produce it is readily available.”
The participants were surveyed between workshops and asked to rank indicators related to the future potentiality of the technology. Interestingly, these rankings looked quite different after the workshops in which the participants were asked to take on the perspective of “imaginary future generations.”
“We noticed that when the “imaginary future generations” method, which has been proven to be effective in facilitating long-term thinking, was adopted, participants perceived the feasibility of this technology differently, and their adoption scenarios changed accordingly,” says Hara.
The study suggests that the simple act of putting ourselves in the position of future generations may provide new perspectives on issues of sustainability and technology, helping us to rethink our priorities and set new directions for research and development.
###
The article, “Assessing future potentiality of technologies from the perspective of ‘imaginary future generations’ – a case study of hydrothermal technology,” was published in Technological Forecasting and Social Change at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2024.123289
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en