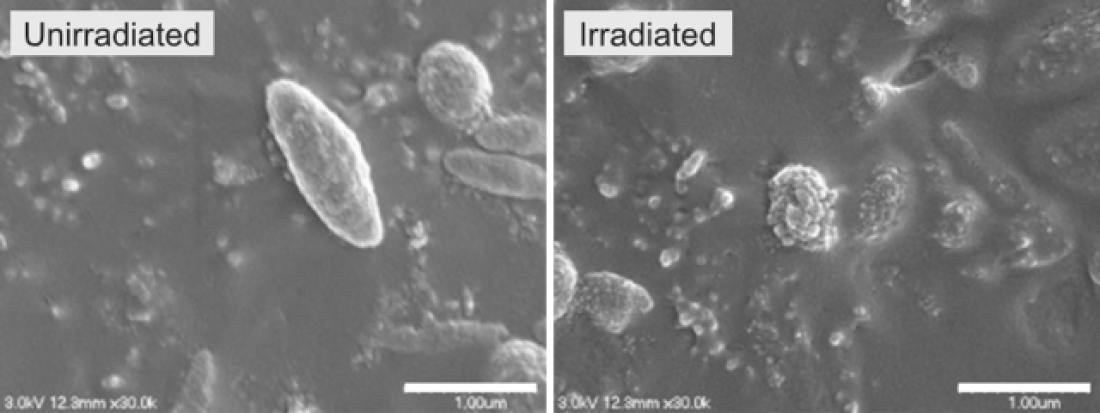
Scanning electron micrographs of melanosomes. Left: Unirradiated melanosomes show a smooth surface. Right: Irradiation by picosecond lasers with a pulse width of 450 ps at a wavelength of 1064 nm and a fluence of 8.50 J/cm² results in melanosomes with their surface structure disrupted.
Many people bothered by skin blemishes might turn to laser treatment. To improve efficacy and reduce complications from such laser treatment, an Osaka Metropolitan University-led research group has developed an index of the threshold energy density, known as fluence, and the dependent wavelength for picosecond lasers.
Picosecond lasers have in recent years been used to remove pigmented lesions. These lasers deliver energy beams in pulses that last for about a trillionth of a second. The lasers target melanosomes, which produce, store, and transport the melanin responsible for pigment.
Postdoctoral Fellow Yu Shimojo of OMU’s Graduate School of Medicine and Specially Appointed Professor Toshiyuki Ozawa and Professor Daisuke Tsuruta of the school’s Department of Dermatology were among the researchers who developed this first picosecond laser index for each of the wavelengths used in clinical practice in treating pigmented lesions.
Comparing previously reported clinical studies, the researchers confirmed that clinical results showing low complication rates and high efficacy can be explained based on these wavelength-dependent indicators.
“The use of this indicator is expected to play an important part in setting irradiation conditions in clinical practice,” Postdoc Fellow Shimojo said. “In addition, the implementation of picosecond laser therapy based on scientific evidence, rather than relying solely on physicians’ experience, is expected to improve the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.”
The findings were published in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is the third largest public university in Japan, formed by the merger of Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in 2022. OMU upholds the “Convergence of Knowledge” through 11 undergraduate schools, a college, and 15 graduate schools. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on X @OsakaMetUniv_en, Instagram, and Facebook.